UNit 1: Graphing and describing data
Definitions:
Dot plot: a graph used when the data is finite-discrete data works best
Stem plot:
-leaves are 1 digit -5-10 stems -can round or truncate data -make a key
Histogram:
-make a frequency table -bin widths must be equal -5-10 bins -bars are touching



Shape of
graphs:
Symmetric: mean=median=mode
Skewed right: mean>median>mode
Skewed left: mean<median<mode
Bi-modal
Uniform
Box Plot:min, Q1, median, Q3, max


Advantages and disadvantages of graphs:
Box plot:
advantage
-can see outliers -quick to make -see 5 # summary
disadvantages
-shape is hard to see -cant see all values -cant see gaps in data
Stem/Split:
advantages
-can see shape -see all values -sample size is present
disadvantages
-some gaps might be hidden -time consuming
Histogram:
advantages
-can see shape -can see gaps -flexible -quick
disadvantages
-dont know all values -changing bin width could change shape
Dot Plot:
advantages
-see all values
disadvantage
-shape is inconclusive -takes more time
Measures of
center:
Mean:average of all the numbers in the data set
-use when graph is symmetric
Median:middle number in a set
-if "n" is odd. median is a number in the data set
-if "n" is even. median is the average of the two middle numbers
-use when graph is skewed
Mode:the number that occurs most in the set
-use when graph is bi-modal
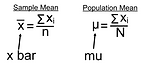

Spread:
How far apart is the data?
Range:maximum-minimum
Inner Quartile Range(IQR): Quartile 3-Quartile 1(Q3-Q1)
Measures of spread:variance
-used to combine multiple data sets
-o²=variance of population
-s²=variance of sample
Outliers:
Outliers:values in a data set that don't follow the general pattern
Upper limit: Q3+1.5(IQR)
Lower limit: Q1-1.5(IQR)
Standard
Deviation:
Standard deviation:average distance from the mean

1.subtract the mean from each value in the data set
2.square all values from step one
3.add all values in step 2
4.divide by n-1
5.take the square root
